The OGC SensorThings API¶
The SensorThings API (STA) is a dedicated Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) standard for making data from IoT-systems available over the web. Version 1.0 was released in 2016 and described the Sensing part [1]. This was extended by a Tasking part in 2019 [2]. Currently, STA is available in version 1.1 [3] while a release of the next version 2.0 is planned for late 2025.
The core of STA consists of a lightweight and generic data model as well as an API that follows the REST-principles. As STA is tailored towards ressource-constrained IoT-appilcations, it also features efficient JSON encoding as well as the usage of MQTT- and OASIS OData protocols.
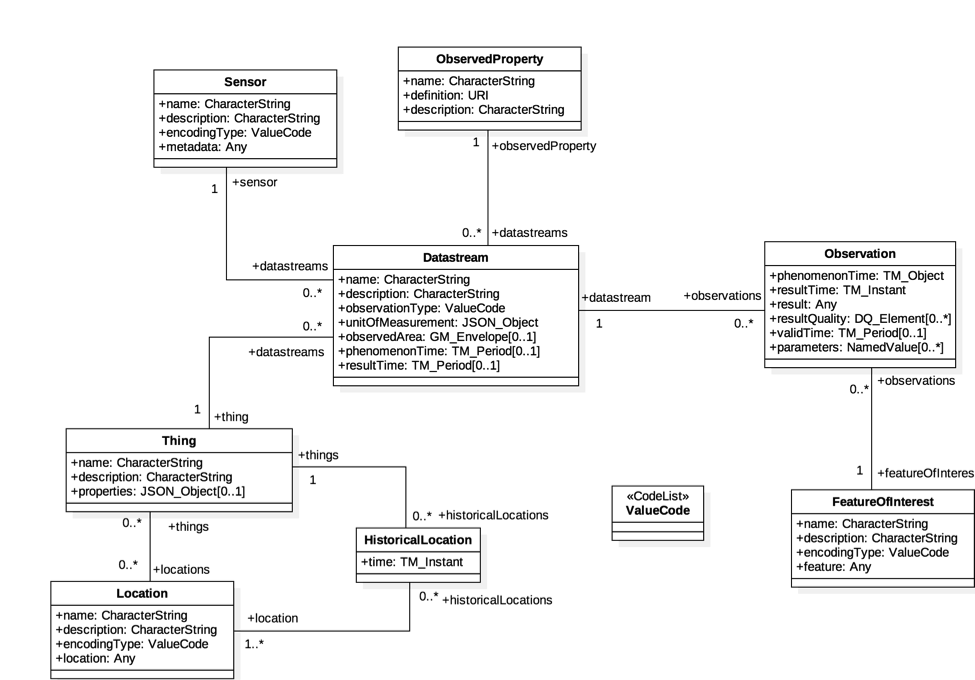
The basic STA data model¶
In this section, we briefly explain the core data model of STA. For further details, please refer to the respective documentation. In general, several entities form the core STA data model: a Thing (e.g., a station) is located at a Location, equipped with one or more Sensors that measure specific ObservedProperties. The resulting Observations are grouped in Datastreams, which provide the structured link between the Sensor, the ObservedProperty, the Thing and the data values over space and time.
Thing¶
A Thing describes the infrastructure that is measuring something, such as a weather station, rover, or complex system with multiple sensors. It anchors all other entities, linking Observations to real-world systems.
Name |
Definition |
Data type |
Multiplicity and use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A property provides a label for Thing entity, commonly a descriptive name. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
This is a short description of the corresponding Thing entity. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
A JSON Object containing user-annotated properties as key–value pairs. |
JSON Object |
Zero-to-one |
Example: An alpine weather station measuring temperature, humidity, and wind.
{
"name": "Alpine Weather Station Wank",
"description": "Automatic station measuring temperature, humidity and wind at 1780m elevation.",
"properties": {
"operator": "KIT/IMK-IFU",
"stationType": "climate"
}
}
Location & Historical Location¶
A Location gives a spatial context to a Thing, while HistoricalLocations record where a Thing was in the past. This makes Observations spatially meaningful and usable in geospatial analysis.
Name |
Definition |
Data type |
Multiplicity and use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Label for the Location. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
Description of the Location. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
Encoding of the |
ValueCode |
One (mandatory) |
|
Location content; type depends on |
Any |
One (mandatory) |
|
A JSON Object containing user-annotated properties as key–value pairs. |
JSON Object |
Zero-to-one |
Example: The GPS coordinates of a drifting ocean buoy, with its track stored as historical locations.
{
"name": "Buoy Position",
"description": "Current GPS location of drifting buoy",
"encodingType": "application/vnd.geo+json",
"location": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [-4.25, 56.87]
},
"properties": {
"deployment": "North Sea 2025"
}
}
Sensor¶
A Sensor is a device, software, or process that generates Observations. It defines how something is measured, ensuring that results are interpretable and comparable across systems.
Name |
Definition |
Data type |
Multiplicity and use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Label for the Sensor. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
Description of the Sensor. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
Encoding of |
ValueCode |
One (mandatory) |
|
Detailed Sensor description; type depends on |
Any |
One (mandatory) |
|
A JSON Object containing user-annotated properties as key–value pairs. |
JSON Object |
Zero-to-one |
Example: A tipping-bucket rain gauge that measures precipitation.
{
"name": "Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge",
"description": "Device measuring precipitation via bucket tips",
"encodingType": "application/pdf",
"metadata": "https://example.org/docs/tbrg-specs.pdf",
"properties": {
"manufacturer": "OTT",
"model": "Pluvio2"
}
}
ObservedProperty¶
An ObservedProperty is the phenomenon being observed, such as air temperature, wind speed, or precipitation. It defines what is being measured in a standardized, interoperable way so that datasets can be compared and combined.
Name |
Definition |
Data type |
Multiplicity and use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A property provides a label for ObservedProperty entity, commonly a descriptive name. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
The URI of the ObservedProperty. Dereferencing this URI SHOULD result in a representation of the definition of the ObservedProperty. |
URI |
One (mandatory) |
|
A description about the ObservedProperty. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
A JSON Object containing user-annotated properties as key–value pairs. |
JSON Object |
Zero-to-one |
Example: Air temperature as defined by the Climate and Forecast (CF) standard name “air_temperature.”
{
"name": "Air Temperature",
"definition": "http://vocab.nerc.ac.uk/standard_name/air_temperature/",
"description": "The bulk temperature of the air",
"properties": {
"cfStandardName": "air_temperature",
"unit": "degree Celsius"
}
}
Datastream¶
A Datastream groups Observations measuring the same ObservedProperty with the same Sensor at one Thing. It links a Sensor, ObservedProperty, and Thing into a coherent, queryable time series.
Name |
Definition |
Data type |
Multiplicity and use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A property provides a label for Datastream entity, commonly a descriptive name. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
The description of the Datastream entity. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
A JSON Object describing the unit of measurement according to UCUM |
JSON Object |
One (mandatory) |
|
The type of Observation, used by the service to encode observations. Value is one of the ValueCode enumeration (see related table). |
ValueCode |
One (mandatory) |
|
A JSON Object containing user-annotated properties as key–value pairs. |
JSON Object |
Zero-to-one |
|
The spatial bounding box for all FeaturesOfInterest in the Observations of this Datastream. |
GM_Envelope (GeoJSON Polygon) |
Zero-to-one (optional) |
|
The temporal interval covering the phenomenon times of all observations in this Datastream. |
TM_Period (ISO 8601 Time Interval) |
Zero-to-one (optional) |
|
The temporal interval covering the result times of all observations in this Datastream. |
TM_Period (ISO 8601 Time Interval) |
Zero-to-one (optional) |
Example: A continuous time series of hourly precipitation values in millimeters from the rain gauge.
{
"name": "Hourly Precipitation",
"description": "Time series of hourly precipitation values in mm",
"unitOfMeasurement": {
"name": "Millimeter",
"symbol": "mm",
"definition": "http://qudt.org/vocab/unit/MilliM"
},
"observationType": "http://www.opengis.net/def/observationType/OGC-OM/2.0/OM_Measurement",
"properties": {
"aggregation": "hourly"
}
}
FeatureOfInterest¶
A FeatureOfInterest is the real-world entity or area to which an Observation applies. It specifies the target of the measurement, such as the air at a specific height, a soil plot, or a river section. This ensures Observations are tied to the correct environmental or spatial feature.
Name |
Definition |
Data type |
Multiplicity and use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A property provides a label for FeatureOfInterest entity, commonly a descriptive name. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
The description about the FeatureOfInterest. |
CharacterString |
One (mandatory) |
|
The encoding type of the feature property. |
ValueCode |
One (mandatory) |
|
The detailed description of the feature. The data type is defined by encodingType. |
Any |
One (mandatory) |
|
A JSON Object containing user-annotated properties as key–value pairs. |
JSON Object |
Zero-to-one |
Example: The air volume at 2 meters above ground at a station site.
{
"name": "Air at 2m height",
"description": "The volume of air at 2m above ground at the station site",
"encodingType": "application/vnd.geo+json",
"feature": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [11.105, 47.555, 2.0]
}
}
Observation¶
An Observation represents a single measurement, including its value and time. It is the core data point that analysis builds upon. Each Observation also links to a FeatureOfInterest, describing the specific entity or area that the Observation relates to (e.g., the air at 2m height, a soil plot, or a river section).
Name |
Definition |
Data type |
Multiplicity and use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
The time instant or interval when the Observation happens (i.e., the time the result applies to the FeatureOfInterest). |
TM_Object (ISO 8601 instant/interval) |
One (mandatory) |
|
The time when the Observation result became available, usually after the phenomenonTime. |
TM_Instant (ISO 8601) |
One (mandatory) |
|
The value of the Observation. The type is determined by the Observation’s Datastream |
Any (depending on observationType) |
One (mandatory) |
|
Describes the quality of the result. |
Any |
Zero-to-many |
|
The time period during which the result is intended to be used. |
TM_Period (ISO 8601 interval) |
Zero-to-one |
|
A JSON Object containing extra key–value pairs that describe additional metadata for the Observation. |
JSON Object |
Zero-to-one |
Example: A single temperature measurement at a given time, with the FeatureOfInterest being the air at 2m above ground.
{
"phenomenonTime": "2025-08-20T10:00:00Z",
"resultTime": "2025-08-20T10:05:00Z",
"result": 12.3,
"FeatureOfInterest": {
"name": "Air at 2m height",
"description": "The volume of air at 2m above ground at the station site",
"encodingType": "application/vnd.geo+json",
"feature": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [11.105, 47.555, 2.0]
}
},
"parameters": {
"unit": "degree Celsius",
"qcFlag": "checked"
}
}
Full Example¶
The following JSON illustrates how all STA entities are linked together in practice, from a Thing with a Location down to its Observations.
{
"Thing": {
"name": "Alpine Weather Station Wank",
"description": "Automatic station measuring temperature, humidity and wind at 1780m elevation.",
"properties": {
"operator": "KIT/IMK-IFU",
"stationType": "climate"
},
"Locations": [
{
"name": "Station Location",
"description": "Fixed location of the weather station",
"encodingType": "application/vnd.geo+json",
"location": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [11.105, 47.555]
}
}
],
"Datastreams": [
{
"name": "Hourly Precipitation",
"description": "Time series of hourly precipitation values in mm",
"unitOfMeasurement": {
"name": "Millimeter",
"symbol": "mm",
"definition": "http://qudt.org/vocab/unit/MilliM"
},
"observationType": "http://www.opengis.net/def/observationType/OGC-OM/2.0/OM_Measurement",
"ObservedProperty": {
"name": "Precipitation",
"definition": "http://vocab.nerc.ac.uk/standard_name/precipitation_amount/",
"description": "Accumulated precipitation depth",
"properties": {
"unit": "millimeter"
}
},
"Sensor": {
"name": "Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge",
"description": "Device measuring precipitation via bucket tips",
"encodingType": "application/pdf",
"metadata": "https://example.org/docs/tbrg-specs.pdf",
"properties": {
"manufacturer": "OTT",
"model": "Pluvio2"
}
},
"Observations": [
{
"phenomenonTime": "2025-08-20T10:00:00Z",
"resultTime": "2025-08-20T10:05:00Z",
"result": 0.8,
"parameters": {
"unit": "mm",
"qcFlag": "checked"
}
},
{
"phenomenonTime": "2025-08-20T11:00:00Z",
"resultTime": "2025-08-20T11:05:00Z",
"result": 1.2,
"parameters": {
"unit": "mm",
"qcFlag": "checked"
}
}
]
}
]
}
}